What Can Lead To Inferior Calcaneal Spur

Overview
Heel spurs are a condition that usually makes its presence known first thing in the morning via heel pain. Discomfort is typically felt in the front and bottom of the heel (calcaneal). Pain can be constant for several months or intermittent for lengthy periods of time.
Causes
Heel spurs develop in some people that have a condition called plantar fasciitis, inflammation of the plantar fascia. Heel spurs form when the plantar fascia separates from the calcaneus. An abnormal bone growth, a hook-like spur, forms from calcium deposits that grow at the site of inflammation. Heel spurs are more common in middle-aged adults and people that have had plantar fasciitis for a long time. People with flat feet or high arches are vulnerable to heel spurs. Women who wear high-heeled shoes are more susceptible, as well.

Symptoms
Heel spurs result in a jabbing or aching sensation on or under the heel bone. The pain is often worst when you first arise in the morning and get to your feet. You may also experience pain when standing up after prolonged periods of sitting, such as work sessions at a desk or car rides. The discomfort may lessen after you spend several minutes walking, only to return later. Heel spurs can cause intermittent or chronic pain.
Diagnosis
Your doctor, when diagnosing and treating this condition will need an x-ray and sometimes a gait analysis to ascertain the exact cause of this condition. If you have pain in the bottom of your foot and you do not have diabetes or a vascular problem, some of the over-the-counter anti-inflammatory products such as Advil or Ibuprofin are helpful in eradicating the pain. Pain creams, such as Neuro-eze, BioFreeze & Boswella Cream can help to relieve pain and help increase circulation.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment of Heel Spurs is the same as treatment of plantar fasciitis. To arrive at an accurate diagnosis, our foot and ankle Chartered Physiotherapists will obtain your medical history and examine your foot. Throughout this process the physio will rule out all the possible causes for your heel pain other than plantar fasciitis. The following treatment may be used. Orthotics/Insoles. Inflammation reduction. Mobilisation. Taping and Strapping. Rest.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery, which is a more radical treatment, can be a permanent correction to remove the spur itself. If your doctor believes that surgery is indicated, he will recommend an operation - but only after establishing that less drastic methods of treatment are not successful.
Prevention
There are heel spur prevention methods available in order to prevent the formation of a heel spur. First, proper footwear is imperative. Old shoes or those that do not fit properly fail to absorb pressure and provide the necessary support. Shoes should provide ample cushioning through the heel and the ball of the foot, while also supporting the arch. Wearing an orthotic shoe insert is one of the best ways to stretch the plantar fascia and prevent conditions such as heel spurs. Stretching the foot and calf is also helpful in preventing damage. Athletes in particular should make sure to stretch prior to any physical activity. Stretching helps prevent heel spurs by making tissue stronger as well as more flexible. In addition, easing into a new or increasingly difficult routine should be done to help avoid strain on the heel and surrounding tissue.
What Causes Bursitis Of The Foot?
Overview
Heel bursitis is also known as retrocalcaneal bursitis. The heel bone is called calcaneus, and the bursa associated with the heel bone is located in the area between the Achilles tendon and calf muscles. When this particular bursa gets aggravated due to constant pressure in the ankle, the posterior end of the heel or the area behind the heel gets inflamed and hence the result is retrocalcaneal bursitis. Strain to the ankles could be caused due to various reasons like extraneous jogging, skipping, or such physical activities that increase the pressure on the ankles.
Causes
Bursitis has many causes, including autoimmune disorders, crystal deposition (gout and pseudogout), infectious diseases, traumatic events, and hemorrhagic disorders, as well as being secondary to overuse. Repetitive injury within the bursa results in local vasodilatation and increased vascular permeability, which stimulate the inflammatory cascade.
Symptoms
When the bursa becomes inflamed after an injury, symptoms usually develop suddenly. When the bursa develops without an injury, symptoms may develop gradually. With both posterior and anterior Achilles tendon bursitis, symptoms usually include swelling and warmth at the back of the heel. A minimally red, swollen, tender spot develops on the back of the heel. When the inflamed bursa enlarges, it appears as a red lump under the skin of the heel and causes pain at and above the heel. If posterior Achilles tendon bursitis becomes chronic, the swelling may become hard, fluid-filled, and red or flesh-colored.
Diagnosis
Your health care provider will take a history to find out if you have symptoms of retrocalcaneal bursitis. Examining your ankle can find the location of the pain. The physician will look for tenderness and redness in the back of the heel. The pain may be worse when the doctor bends the ankle upward (dorsiflex). Or, the pain may be worse when you rise on your toes. You will not usually need imaging studies such as x-ray and MRI at first. If the first treatment does not improve the symptoms, your health care provider may recommend these tests. MRI may show inflammation.
Non Surgical Treatment
Over-the-counter or custom heel wedges may help to decrease the stress placed on the attachment of the achilles tendon and the associated bursa. If these interventions are ineffective, then some health care providers may inject a small amount of steroids into the bursa. If the condition is associated with Achilles tendonitis, then casting the ankle to prevent motion for several weeks can be effective. Very rarely, surgery may be necessary to remove the inflamed bursa.
Surgical Treatment
Only if non-surgical attempts at treatment fail, will it make sense to consider surgery. Surgery for retrocalcanel bursitis can include many different procedures. Some of these include removal of the bursa, removing any excess bone at the back of the heel (calcaneal exostectomy), and occasionally detachment and re-attachment of the Achilles tendon. If the foot structure and shape of the heel bone is a primary cause of the bursitis, surgery to re-align the heel bone (calcaneal osteotomy) may be considered. Regardless of which exact surgery is planned, the goal is always to decrease pain and correct the deformity. The idea is to get you back to the activities that you really enjoy. Your foot and ankle surgeon will determine the exact surgical procedure that is most likely to correct the problem in your case. But if you have to have surgery, you can work together to develop a plan that will help assure success.
Do Hammer Toes Hurt
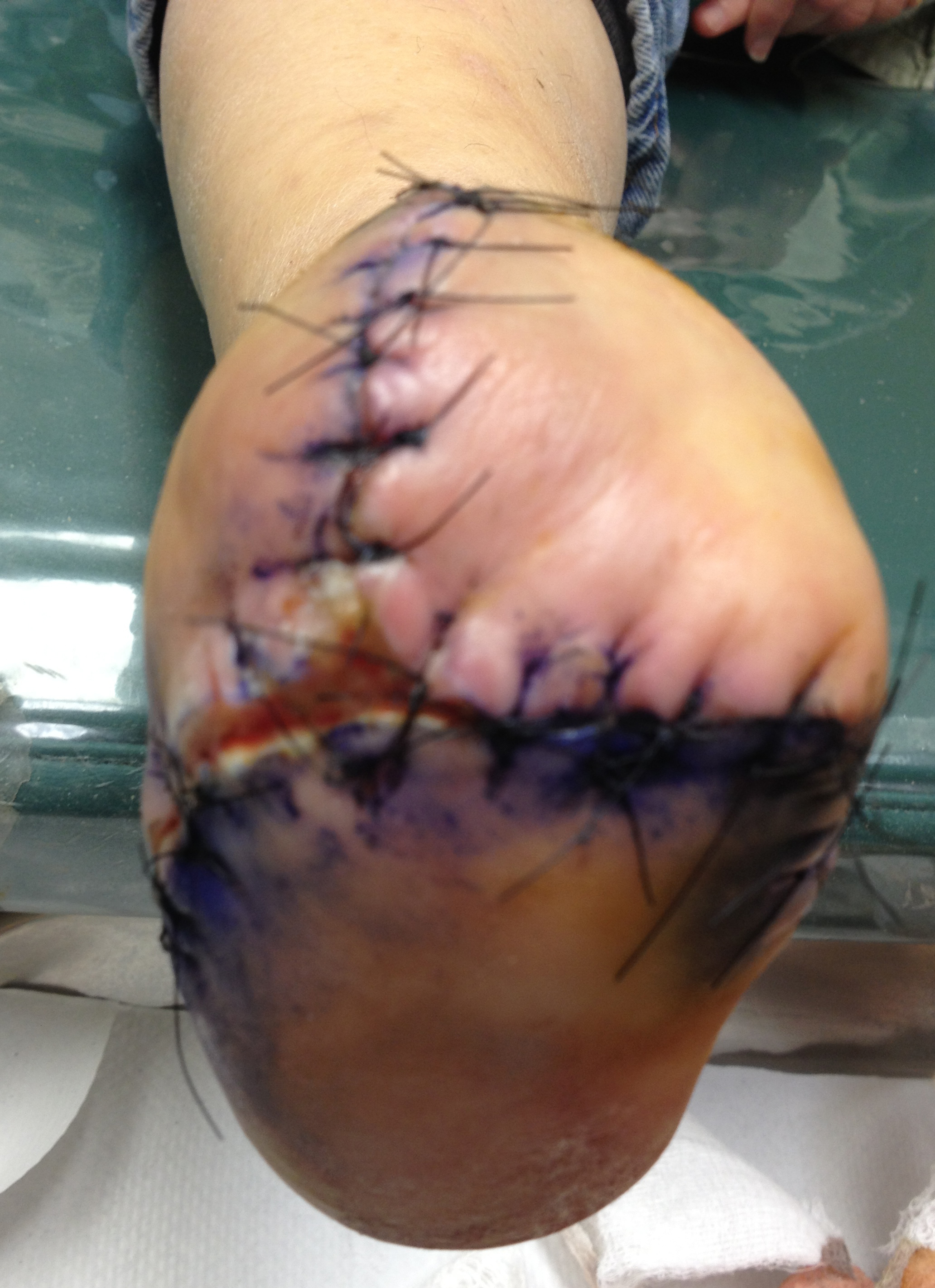 Overview
Overview
A hammertoes is a deformity of the second, third or fourth toes in which the main toe joint is bent upward like a claw. Initially, hammertoes are flexible and can be corrected with simple measures. Left untreated, they can become fixed and require surgery. Hammertoe results from shoes that don?t fit properly or a muscle imbalance, usually in combination with one or more other factors. Muscles work in pairs to straighten and bend the toes. If the toe is bent and held in one position long enough, the muscles tighten and can?t stretch out.
Causes
The cause of hammertoes varies, but causes include genetics, arthritis and injury to the toe. Treatment for hammertoes depends on the severity and can include anti-inflammatory medication, metatarsal pads, foot exercises and better-fitting shoes. If the pain caused by a hammertoe is so severe that wearing a shoe is uncomfortable, surgery may be necessary. Typically this surgery is an outpatient procedure that doesn?t require general anesthesia, though it is an option. Recovery from surgery usually takes a few weeks, and patients are given special shoes to wear.
 Symptoms
Symptoms
A toe (usually the second digit, next to the big toe) bent at the middle joint and clenched into a painful, clawlike position. As the toe points downward, the middle joint may protrude upward. A toe with an end joint that curls under itself. Painful calluses or corns. Redness or a painful corn on top of the bent joint or at the tip of the affected toe, because of persistent rubbing against shoes Pain in the toes that interferes with walking, jogging, dancing, and other normal activities, possibly leading to gait changes.
Diagnosis
Your healthcare provider will examine your foot, checking for redness, swelling, corns, and calluses. Your provider will also measure the flexibility of your toes and test how much feeling you have in your toes. You may have blood tests to check for arthritis, diabetes, and infection.
Non Surgical Treatment
Inserts in your shoes can be used to help relieve pressure on the toes from the deformity. Splints/Straps. These can be used to help re-align and stretch your toes and correct the muscle imbalance and tendon shortening. One of the most common types are toe stretchers like the yogatoe. Chiropody. A chiropodist can remove calluses or corns, areas of hard skin that have formed to make the foot more comfortable.Steroid injections can help to reduce pain and inflammation.
Surgical Treatment
For the surgical correction of a rigid hammertoe, the surgical procedure consists of removing the damaged skin where the corn is located. Then a small section of bone is removed at the level of the rigid joint. The sutures remain in place for approximately ten days. During this period of time it is important to keep the area dry. Most surgeons prefer to leave the bandage in place until the patient's follow-up visit, so there is no need for the patient to change the bandages at home. The patient is returned to a stiff-soled walking shoe in about two weeks. It is important to try and stay off the foot as much as possible during this time. Excessive swelling of the toe is the most common patient complaint. In severe cases of hammertoe deformity a pin may be required to hold the toe in place and the surgeon may elect to fuse the bones in the toe. This requires several weeks hammertoe of recovery.
Hammer Toe Repair
A Hammer toe is a deformity of the second, third or fourth toe in which the toe becomes bent at the middle joint; hence, it resembles a hammer. Claw toe and mallet toe are related conditions. While a hammer toe is contracted at the first toe joint, a mallet toe is contracted at the second toe joint, and a claw toe is contracted at both joints. According to the 2012 National Foot Health Assessment conducted by the NPD Group for the Institute for Preventive Foot Health, 3 percent of U.S. adults age 21 and older (about 7 million people) have experienced hammer toe or claw toe. The condition is significantly more prevalent in females than in males.
Causes
Hereditary and shoe gear are probably the most likely reasons to develop a hammer toe. Tight pointy shoes may cause a hammer toes. High heels also can cause hammer toes. A deformed toe often develops over time, and certain types of feet may be predisposed. Some patients may develop a hammer toe or cross over toe (of the 2nd toe) due to a bunion of the big toe.
 Symptoms
Symptoms
Pain on the bottom of your foot, especially under the ball of your foot, is one of the most common symptoms associated with hammertoes. Other common signs and symptoms of hammertoes include pain at the top of your bent toe from footwear pressure. Corns on the top of your bent toe. Redness and swelling in your affected area. Decreased joint range of motion in your affected toe joints.
Diagnosis
Hammertoes are progressive, they don?t go away by themselves and usually they will get worse over time. However, not all cases are alike, some hammertoes Hammer toe progress more rapidly than others. Once your foot and ankle surgeon has evaluated your hammertoes, a treatment plan can be developed that is suited to your needs.
Non Surgical Treatment
To keep your hammertoes more comfortable, start by replacing your tight, narrow, pointy shoes with those that have plenty of room in the toes. Skip the high heels in favor of low-heeled shoes to take the pressure off your toes. You should have at least one-half inch between your longest toe and the tip of your shoe. If you don't want to go out and buy new shoes, see if your local shoe repair shop can stretch your shoes to make the toe area more accommodating to your hammertoe.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery to straighten the toe may be needed if an ulcer has formed on either the end or the top surface of the toe. Surgery sometimes involves cutting the tendons that support movement in the toe so that the toe can be straightened. Cutting the tendons, however, takes away the ability to bend the very end of the toe. Another type of surgery combines temporary insertion of a pin or rod into the toe and alteration or repair of the tendons, so that the toe is straightened. After surgery, the deformity rarely recurs.
.jpg) Prevention
Prevention
Walking barefoot increases the risk for injury and infection. Being on your feet throughout the day can cause them to swell, this is the best time to buy shoes to get a better fit. Do not buy shoes that feel tight. Do not buy shoes that ride up and down your heel as you walk. The ball of your foot should fit into the widest part of the shoe. Remember, the higher the heel the less safe the shoe will be. Avoid shoes with pointed or narrow toes. If the shoes hurt, do not wear them. If you start noticing the beginning signs of hammer toes, you may still be able to prevent the tendons from tightening by soaking your feet every day in warm water, wearing toe friendly shoes, and performing foot exercises such as stretching your toes and ankles. A simple exercise such as placing a small towel on the floor and then picking it up using only your toes can help to restore the flexibility of tendons.
Hammer Toe Repair Surgery
 Overview
Overview
The name hammertoe comes from the way the tip of the toe hits or hammers on the floor with each step. The primary deformity seen in a hammer toe is found at the PIPJ (proximal interphalangeal joint) which is the first or more proximal of the two joints of the toe. A mallet toe, on the other hand, is a similar deformity but is found in the DIPJ (distal interphalangeal joint). And lastly, claw toes are a deformity where the entire toe grabs and involves the MPJ (metatarsal phalangeal joint) PIPJ and DIPJ. Collectively, these deformities are referred to as hammer toes. Hammer toes can affect one or all of the toes simultaneously.
Causes
Hammer toe results from shoes that don?t fit properly or a muscle imbalance, usually in combination with one or more other factors. Muscles work in pairs to straighten and bend the toes. If the toe is bent and held in one position long enough, the muscles tighten and cannot stretch out. Some other causes are diabetes, arthritis, neuromuscular disease, polio or trauma.
 Symptoms
Symptoms
If the toes remain in the hammertoe position for long periods, the tendons on the top of the foot will tighten over time because they are not stretched to their full length. Eventually, the tendons shorten enough that the toe stays bent, even when shoes are not being worn. The symptoms of hammertoe include a curling toe, pain or discomfort in the toes and ball of the foot or the front of the leg, especially when toes are stretched downward, thickening of the skin above or below the affected toe with the formation of corns or calluses, difficulty finding shoes that fit well. In its early stages, hammertoe is not obvious. Frequently, hammertoe does not cause any symptoms except for the claw-like toe shape.
Diagnosis
The exam may reveal a toe in which the near bone of the toe (proximal phalanx) is angled upward and the middle bone of the toe points in the opposite direction (plantar flexed). Toes may appear crooked or rotated. The involved joint may be painful when moved, or stiff. There may be hammertoe areas of thickened skin (corns or calluses) on top of or between the toes, a callus may also be observed at the tip of the affected toe beneath the toenail. An attempt to passively correct the deformity will help elucidate the best treatment option as the examiner determines whether the toe is still flexible or not. It is advisable to assess palpable pulses, since their presence is associated with a good prognosis for healing after surgery. X-rays will demonstrate the contractures of the involved joints, as well as possible arthritic changes and bone enlargements (exostoses, spurs). X-rays of the involved foot are usually performed in a weight-bearing position.
Non Surgical Treatment
Your doctor will decide what type of hammertoe you have and rule out other medical conditions. Treatment may range from more appropriate footgear to periodic trimming and padding of the corn. Cortisone injections may be indicated if a bursitis is present. Antibiotics may be utilized in the presence of infection. Removable accommodative pads may be made for you.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is the approach that is often necessary to correct hammertoe that fails to respond to nonsurgical management. Surgery is appropriate when the muscles and tendons involved in a hammertoe problem have become so tight that the joints are rigid, misaligned and unmovable. There are a number of surgical techniques for dealing with the complex range of joint, bone, muscle, tendon and ligament abnormalities that define each hammertoe's make-up. To correct a hammertoe deformity, the surgeon's goal is to restore the normal alignment of the toe joint, relieving the pressure that led to the hammertoe's development (this should also relieve the pain, as well). To do this, he or she may remove part of the boney structure that creates a prominence at the top of the joint. Tighten or loosen the muscles, tendons and ligaments around the toe joints. Realign the toe bones by cutting one or more and shifting their position, realigning muscles, tendons and ligaments accordingly. Use screws, wires or plates to hold the joint surfaces together until they heal. Reconstruct a badly damaged joint or replace it with an artificial implant.
Discover More About Over-Pronation
Overview
Over-pronation occurs when the foot collapses too far inward stressing the plantar fascia (the area underneath the arch of the foot.) Normally, one pronates every time he/she walks, but excessive pronation is called over-pronation. When this occurs it can cause pain in the feet, knees, hips, low back and even the shoulder.

Causes
Pronation can occur as an overuse syndrome in active runners, where a great deal of stress is placed on ligaments and tendons that support the medial column. Obesity is another predictor for pronation and deterioration of the medial ligaments and posterior tibial tendon due to excessive stress on these tissues. Acute Trauma can also lead to over-pronation when ligaments are torn or tendon is ruptured. Once again this can lead to a collapse of the medial column. Arthritic conditions involving the knee joint when the joint is in varus (inner collapse) posture, this places the center of gravity over the ankle joint rather than the foot causing undue pressure on the inner ankle.
Symptoms
Overpronation can lead to injuries and pain in the foot, ankle, knee, or hip. Overpronation puts extra stress on all the bones in the feet. The repeated stress on the knees, shins, thighs, and pelvis puts additional stress on the muscles, tendons, and ligaments of the lower leg. This can put the knee, hip, and back out of alignment, and it can become very painful.
Diagnosis
Do the wet foot test. Get your feet wet and walk along a paved surface or sand and look at the footprints you leave. If you have neutral feet you will see a print of the heel with a thin strip connecting to your forefoot, but if you're overpronating your foot print will look a bit like a giant blob with toes.
Non Surgical Treatment
Over-Pronation can be treated conservatively (non-surgical treatments) with over-the-counter orthotics. This orthotics should be designed with appropriate arch support and medial rear foot posting to prevent the over-pronation. Footwear should also be examined to ensure there is a proper fit. Footwear with a firm heel counter is often recommended for extra support and stability. Improperly fitting footwear can lead to additional foot problems. If the problem persists, consult your foot doctor.
Surgical Treatment
Hyperpronation can only be properly corrected by internally stabilizing the ankle bone on the hindfoot bones. Several options are available. Extra-Osseous TaloTarsal Stabilization (EOTTS) There are two types of EOTTS procedures. Both are minimally invasive with no cutting or screwing into bone, and therefore have relatively short recovery times. Both are fully reversible should complications arise, such as intolerance to the correction or prolonged pain. However, the risks/benefits and potential candidates vary. Subtalar Arthroereisis. An implant is pushed into the foot to block the excessive motion of the ankle bone. Generally only used in pediatric patients and in combination with other procedures, such as tendon lengthening. Reported removal rates vary from 38% - 100%, depending on manufacturer. HyProCure Implant. A stent is placed into a naturally occurring space between the ankle bone and the heel bone/midfoot bone. The stent realigns the surfaces of the bones, allowing normal joint function. Generally tolerated in both pediatric and adult patients, with or without adjunct soft tissue procedures. Reported removal rates, published in scientific journals vary from 1%-6%.
Does Calcaneal Apophysitis Always Demand Surgery Treatment?
Overview
Sever's disease (calcaneal apophysitis) is a common cause of heel pain, particularly in physically active young people who are about to begin puberty. The cause is uncertain, but it is thought that the long calf bones of the leg grow faster than the surrounding muscle and soft tissue, causing the Achilles tendon to pull uncomfortably tight. Sever?s disease (sometimes called Sever disease) is a common cause of heel pain, particularly in the young and physically active. It usually develops just before puberty. Boys are slightly more prone to this condition than girls. Physiotherapy can help manage the symptoms of Sever?s disease so that the young person can continue to take part in physical activity. Another name for Sever?s disease is calcaneal apophysitis.
Causes
During the growth spurt of early puberty, the heel bone (also called the calcaneus) sometimes grows faster than the leg muscles and tendons. This can cause the muscles and tendons to become very tight and overstretched, making the heel less flexible and putting pressure on the growth plate. The Achilles tendon (also called the heel cord) is the strongest tendon that attaches to the growth plate in the heel. Over time, repeated stress (force or pressure) on the already tight Achilles tendon damages the growth plate, causing the swelling, tenderness, and pain of Sever's disease. Such stress commonly results from physical activities and sports that involve running and jumping, especially those that take place on hard surfaces, such as track, basketball, soccer, and gymnastics.
Symptoms
The main symptom of sever's disease is pain and tenderness at the back of the heel which is made worse with physical activity. Tenderness will be felt especially if you press in or give the back of the heel a squeeze from the sides. There may be a lump over the painful area. Another sign is tight calf muscles resulting with reduced range of motion at the ankle. Pain may go away after a period of rest from sporting activities only to return when the young person goes back to training.
Diagnosis
Sever disease is most often diagnosed clinically, and radiographic evaluation is believed to be unnecessary by many physicians, but if a diagnosis of calcaneal apophysitis is made without obtaining radiographs, a lesion requiring more aggressive treatment could be missed. Foot radiographs are usually normal and the radiologic identification of calcaneal apophysitis without the absence of clinical information was not reliable.
Non Surgical Treatment
If your child is diagnosed with Sever's disease, treatment is fairly straightforward. He or she should avoid any activities that cause a flare-up of heel pain. Treat the pain with ice for 20 minutes, three times a day. If the pain is severe, over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen can be used for a short period of time. (Don't use aspirin in a child or teen because it can result in a rare but life-threatening condition called Reye's syndrome.) In some instances, a child might have other foot problems, as well, such as high arches, flat feet, or bowed legs. In these instances, your doctor can recommend an orthotic device to help further prevent the pain related to Sever's disease. One other simple tip that can prevent Sever's disease or speed along recovery is for your child to wear supportive shoes and avoid going barefoot as much as possible.
Surgical Treatment
The surgeon may select one or more of the following options to treat calcaneal apophysitis. Reduce activity. The child needs to reduce or stop any activity that causes pain. Support the heel. Temporary shoe inserts or custom orthotic devices may provide support for the heel. Medications. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, help reduce the pain and inflammation. Physical therapy. Stretching or physical therapy modalities are sometimes used to promote healing of the inflamed issue. Immobilization. In some severe cases of pediatric heel pain, a cast may be used to promote healing while keeping the foot and ankle totally immobile. Often heel pain in children returns after it has been treated because the heel bone is still growing. Recurrence of heel pain may be a sign of calcaneal apophysitis, or it may indicate a different problem. If your child has a repeat bout of heel pain, be sure to make an appointment with your foot and ankle surgeon.
Functional Leg Length Discrepancy Test
Overview
Having one leg shorter than the other is a common physical condition. It has two primary causes--structural or functional problems. Structural differences in length can be the result of growth defect, previous injuries or surgeries. Functional differences in length can result from altered mechanics of the feet, knee, hip and/or pelvis. These altered mechanics from functional leg length discrepancy often stem from having an unbalanced foundation.

Causes
Some causes of leg length discrepancy (other than anatomical). Dysfunction of the hip joint itself leading to compensatory alterations by the joint and muscles that impact on the joint. Muscle mass itself, i.e., the vastus lateralis muscle, pushes the iliotibial band laterally, causing femoral compensations to maintain a line of progression during the gait cycle. This is often misdiagnosed as I-T band syndrome and subsequently treated incorrectly. The internal rotators of the lower limb are being chronically short or in a state of contracture. According to Cunningham's Manual of Practical Anatomy these are muscles whose insertion is lateral to the long axis of the femur. The external rotators of the hip joint are evidenced in the hip rotation test. The iliosacral joint displays joint fixations on the superior or inferior transverse, or the sagittal axes. This may result from many causes including joint, muscle, osseous or compensatory considerations. Short hamstring muscles, i.e., the long head of the biceps femoris muscle. In the closed kinetic chain an inability of the fibula to drop inferior will result in sacrotuberous ligament loading failure. The sacroiliac joint dysfunctions along its right or left oblique axis. Failure or incorrect loading of the Back Force Transmission System (the longitudinal-muscle-tendon-fascia sling and the oblique dorsal muscle-fascia-tendon sling). See the proceedings of the first and second Interdisciplinary World Congress on Low Back Pain. Sacral dysfunction (nutation or counternutation) on the respiratory axis. When we consider the above mentioned, and other causes, it should be obvious that unless we look at all of the causes of leg length discrepancy/asymmetry then we will most assuredly reach a diagnosis based on historical dogma or ritual rather than applying the rules of current differential diagnosis.
Symptoms
Children whose limbs vary in length often experience difficulty using their arms or legs. They might have difficulty walking or using both arms to engage in everyday activities.
Diagnosis
Asymmetry is a clue that a LLD is present. The center of gravity will shift to the short limb side and patients will try to compensate, displaying indications such as pelvic tilt, lumbar scoliosis, knee flexion, or unilateral foot pronation. Asking simple questions such as, "Do you favor one leg over the other?" or, "Do you find it uncomfortable to stand?" may also provide some valuable information. Performing a gait analysis will yield some clues as to how the patient compensates during ambulation. Using plantar pressure plates can indicate load pressure differences between the feet. It is helpful if the gait analysis can be video-recorded and played back in slow motion to catch the subtle aspects of movement.
Non Surgical Treatment
For minor limb length discrepancy in patients with no deformity, treatment may not be necessary. Because the risks may outweigh the benefits, surgical treatment to equalize leg lengths is usually not recommended if the difference is less than 1 inch. For these small differences, the physician may recommend a shoe lift. A lift fitted to the shoe can often improve walking and running, as well as relieve any back pain that may be caused by the limb length discrepancy. Shoe lifts are inexpensive and can be removed if they are not effective.

Surgical Treatment
Surgeries to lengthen a leg are generally only performed when there is a difference in leg length of greater than four centimeters. These types of surgeries can be more difficult and have more complications, such as infections, delayed healing, dislocations, and high blood pressure. In a several step process, bone lengthening surgeries involve cutting a bone in two in order to allow new bone growth to occur. After the bone is cut, a special apparatus is worn with pins that will pull the bone apart at approximately one millimeter per day. This causes osteogenesis, or new bone growth, in between the cut bone segments. A cast or brace may be required for several months after surgery to allow the new bone growth to harden and provide extra support.